In this article, readers will gain an understanding of a variety of sliding door configurations, including single, double, telescopic, stacking, and curved sliding doors. The article discusses the various components that make up a sliding door system, such as door panels, handles, tracks, guides, and seals. Additionally, it covers materials commonly used in sliding doors, including wood, aluminium, steel, vinyl, and fiberglass. The advantages of different sliding door configurations are also examined, such as their space-saving design, improved indoor-outdoor flow, and enhanced aesthetic appeal. Furthermore, readers will learn how to choose the right sliding door configuration based on factors like available space, design preferences, and budget. Lastly, the article offers guidance on the installation and maintenance of sliding door systems, ensuring proper care and longevity.
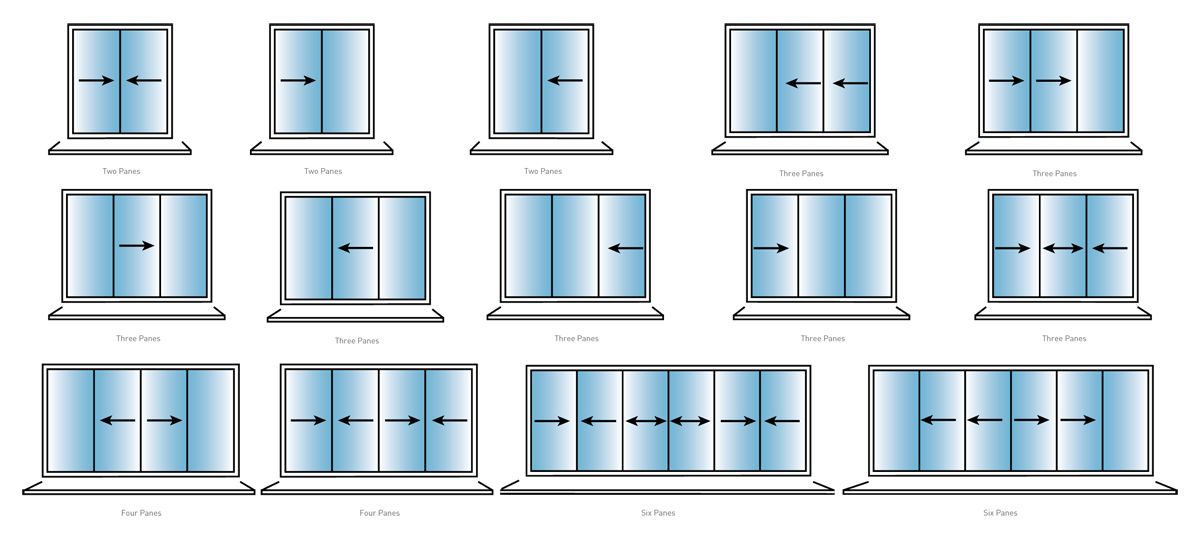
Image Source: bifoldnetwork.com
Single Sliding Doors
Single sliding doors are the most basic and widespread type of sliding door configuration. They consist of a single door panel that slides along a track parallel to a fixed panel, either an adjacent wall or another non-moving door panel. The sliding door is equipped with rollers located at the top or bottom of the door, allowing it to glide smoothly along the track.
This configuration is most often used for residential settings where space is limited, such as small rooms, closets, and entranceways. Single sliding doors offer several advantages, including:
– Space-saving design, as they do not require a door swing area
– Easy installation and maintenance
– Cost-effectiveness, as they are relatively inexpensive to purchase and install
Some common downsides of single sliding doors include:
– Limited access to the doorway, as only half of the opening will be accessible when the door is open
– Potential issues with sealing and weatherproofing, as there may be gaps between the sliding door and the adjacent wall or fixed panel
Double Sliding Doors
Double sliding doors, also known as bi-parting or tandem doors, consist of two door panels that slide along parallel tracks away from each other, opening up the full doorway. Like single sliding doors, this configuration can have rollers at the top or bottom, ensuring smooth operation.
This configuration is often found in commercial buildings, larger residential homes, or spaces with wide doorways. Double sliding doors offer several advantages, including:
– Greater access to the doorway, as both panels slide away, providing a full-width opening
– Enhanced aesthetics, as they can create an elegant and symmetrical appearance
– Increased versatility, as they can be used for exterior or interior applications, such as patios, closets, or conference rooms
However, double sliding doors also come with a few downsides:
– Higher costs for purchasing and installing, as they require more materials and hardware than single sliding doors
– More complex installation process, as the alignment of both panels must be perfect to ensure smooth operation
– Additional maintenance due to the increased number of moving parts and hardware
Telescopic Sliding Doors
Telescopic sliding doors, also known as multi-slide doors, feature multiple door panels that slide along parallel tracks, stacking behind one another as they open. This configuration allows for a larger opening than single or double sliding doors, making them ideal for areas with wide doorways or where maximum access is desired.
Telescopic sliding doors are commonly used in commercial spaces, such as retail stores, hotels, and offices, as well as high-end residential homes. The advantages of this configuration include:
– Maximum doorway access, as multiple panels slide and stack, creating larger openings than single or double sliding doors
– Customizability, as the number of panels and tracks can be configured to fit specific requirements
– Enhanced visual appeal, due to the seamless integration between the panels and the tracks
The disadvantages of telescopic sliding doors include:
– Higher costs, as they require more materials, hardware, and installation expertise than single or double sliding doors
– More complex installation and maintenance, due to the increased number of panels and tracks
– Reduced energy efficiency, as it can be difficult to create an airtight seal between panels and tracks.
Sliding Pocket Doors
Sliding pocket doors are a unique type of sliding door that slides into a recessed pocket within the wall when opened. This configuration offers a clean design and maximum space-saving capabilities, as the door disappears entirely into the wall when opened.
Pocket doors are typically used in small residential spaces where even the minimal space taken up by traditional sliding doors is too much or where a clean, unobstructed look is desired. Advantages of sliding pocket doors include:
– Maximum space-saving, as the door completely disappears into the wall when opened
– Unobstructed views and access to the doorway, as there is no visible door panel or track when the door is open
– Ability to incorporate a variety of door styles, finishes, and hardware into the design
The downsides of sliding pocket doors include:
– Complex installation, as the pocket must be created within the wall, which may require structural alterations
– Increased costs, as the installation process is more labor-intensive and often requires hiring professionals
– Maintenance challenges, as accessing the track and hardware within the wall may be difficult or require removal of portions of the wall.
Types of Sliding Door Configurations
Sliding doors are an elegant and efficient solution to space limitations in both residential and commercial settings. They are stylish, modern, and can be easily customized to meet various aesthetic and functional needs. Sliding doors are available in a range of configurations, each with its own unique set of advantages and applications. Let’s take a closer look at the various types of sliding door configurations available in the market.
Single Sliding Doors
Single sliding doors are the most straightforward and common type of sliding door configuration. As the name suggests, a single sliding door consists of a single door panel that slides along a track or rail. One side of the door remains stationary, while the other slides open and closed.
This configuration is suitable for spaces with limited room for door swing or where a sliding door provides a more convenient and space-saving solution. Single sliding doors are commonly used in bathrooms, closets, balconies, and other small openings that require a door. They come in various materials, such as aluminium, glass, wood, or a combination of these, providing several design options to match any interior style.
Double Sliding Doors
Double sliding doors consist of two door panels that slide in opposite directions when opening or closing. These doors slide along parallel tracks or rails, with one door panel sliding behind the other. When both doors are fully opened, the opening is approximately double the width of a single sliding door.
Double sliding doors provide a larger opening, making it perfect for wide entrances or partitioning large spaces. They are commonly used in living rooms, dining rooms, patios, or commercial spaces such as offices and conference rooms. Double sliding doors offer better sound and heat insulation than single sliding doors due to the double-layered door panels. They come in various materials like glass, wood, or aluminium to complement different interior styles.
Telescopic Sliding Doors
Telescopic sliding doors are an advanced sliding door solution that allows for a wide opening with a minimal footprint. These doors consist of multiple door panels that slide along a single track or rail. As the first panel moves, it pulls the other panels along, causing them to slide together, stacking beside one another when fully opened.
Telescopic sliding doors are suitable for spaces where a wide and unobstructed opening is necessary but limited space for door panels to slide along the track is available. They are commonly used in commercial settings, such as offices, shops, airports, and other public spaces that require wide entrances for easy access and traffic flow. Their modern design and smooth operation make telescopic sliding doors an eye-catching and practical solution for any space.
Stacking Sliding Doors
Stacking sliding doors consist of multiple door panels that slide along individual tracks, stacking one behind the other when opened. These doors provide a wide opening while allowing for better control over the amount of space opened. They are an excellent solution for spaces that require a large and seamless connection to the outdoors, such as patios, pool areas, and home extensions.
Stacking sliding doors offer versatility in design, with options to add or remove door panels to suit specific needs. These doors also provide better sound and heat insulation than other sliding door configurations, thanks to the multiple layers of door panels. They are available in various materials, such as aluminium, glass, and wood, to match different design aesthetics.
Curved Sliding Doors
Curved sliding doors are a unique and visually striking door configuration. They consist of curved door panels that slide and pivot along a curved track or rail. These doors can create a fluid and seamless connection between spaces while offering an elegant and eye-catching design element.
Curved sliding doors are perfect for spaces with curved walls or openings that need a unique and sophisticated touch. They can be used in various settings, including residential, commercial, and public spaces, such as shopping centers, hotels, and office buildings. Curved sliding doors are available in different materials and finishes, providing a wide range of design possibilities to complement any space.
Components of Sliding Door Configurations
Sliding doors are a popular choice for both residential and commercial spaces due to their space-saving and aesthetic attributes. However, these doors are made up of various components that need to work together seamlessly to ensure smooth operation. This article will delve into the different components of sliding door configurations, including the door panel and glass, handles and locks, tracks and rollers, guides and stops, as well as weather seals.
Door Panel and Glass
The door panel and glass are the main elements of a sliding door system. Typically, the door panel is made from materials like wood, aluminium, steel, or vinyl. The choice of material often depends on factors such as the desired aesthetic, budget, and insulation properties required. Some sliding door panels have a solid design, while others may feature glass inserts or be entirely made of glass.
Glass is a common choice for sliding doors due to its ability to let in natural light, provide unobstructed views, and create a connection between the interior and exterior spaces. There are various types of glass available for sliding doors, including clear, tinted, low-emissivity, and laminated glass. The choice of glass can have an impact on factors like energy efficiency, UV protection, privacy, and safety.
For instance, low-emissivity glass has a special coating that reflects heat and helps regulate the temperature inside the building, making it more energy-efficient. Tinted glass can reduce the amount of sunlight entering the space and provide increased privacy, while laminated glass has a layer of plastic between the glass panes for added safety and noise reduction.
Door Handles and Locks
Door handles and locks are crucial components of sliding doors, ensuring security and accessibility. Handles come in various styles and materials, such as modern stainless steel or traditional brass. Depending on the design, some handles may feature a built-in lock, while others have a separate lock mechanism.
Locks for sliding doors can be categorized into key locks, latch locks, and electronic locks. Key locks typically involve a traditional key-operated locking mechanism, while latch locks operate by engaging a latch into a strike plate. Electronic locks incorporate technologies such as keypads or smart systems, allowing for keyless entry or remote access.
Some sliding door configurations also feature a secondary lock, known as a foot or vent lock, which can be engaged from the inside when the door is partially open. This allows for ventilation without compromising security.
Tracks and Rollers
Tracks and rollers are essential components for the smooth operation of sliding doors. The track is usually made of metal or plastic and can be mounted on the floor, wall, or overhead, depending on the door configuration. Rollers are attached to the bottom or top of the door panel, allowing the door to glide effortlessly along the track.
There are different types of roller configurations, such as single or double rollers, as well as adjustable or fixed rollers. Adjustable rollers can be fine-tuned to ensure the door remains aligned and runs smoothly on the track, while fixed rollers offer a more simple and cost-effective solution. Roller materials also vary, with options like nylon, steel, or stainless steel, each with its own benefits and drawbacks in terms of durability, noise, and maintenance requirements.
Guides and Stops
Guides and stops are important components to keep the sliding door in place and prevent it from coming off the track. Guides typically consist of a bracket or channel attached to the door frame, ensuring the door panel stays aligned as it slides along the track. These guides can be made from plastic, metal, or a combination of both materials.
Stops are used to halt the movement of the door at either end of the track, preventing it from slamming into the frame or completely coming off the track. Stops can be a simple rubber bumper or a more advanced magnetic or cushioned stop that absorbs the door’s momentum for a soft and controlled closure.
Weather Seals
Weather seals play a vital role in maintaining energy efficiency and comfort in the space enclosed by sliding doors. These seals typically consist of rubber, vinyl, or foam strips that are installed along the edges of the door panel and frame. The purpose of these seals is to eliminate gaps that could allow air, water, or debris to enter the interior.
Weather seals not only help in keeping the interior space comfortable and free from drafts but also protect the door components from damage caused by water infiltration or dust accumulation. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and lubrication, as well as timely replacement of damaged or worn-out seals, is crucial to ensuring the long-lasting performance of your sliding door configuration.
Sliding Door Materials
Sliding doors are a stylish and functional addition to any home, office, or commercial space. They provide a seamless transition from one room to another while maximizing the available space. One of the critical factors to consider when choosing the right sliding door for your space is the material. The type of material will not only affect the door’s aesthetic appeal and durability but also its energy efficiency and maintenance requirements. This article will explore the different sliding door materials, including wood, aluminium, steel, vinyl, and fiberglass to help you make an informed decision.
Wood
Wooden sliding doors have been a popular choice for many years due to their natural beauty, warmth, and versatility. They can be easily customized in terms of size, style, and finish to match various décor schemes. The most common types of wood used for sliding doors include oak, mahogany, maple, cherry, and walnut.
However, wooden doors require more maintenance than other materials to prevent warping, rotting, or termite damage. Regular cleaning, painting, or staining is necessary to maintain their appearance and prevent deterioration. Wood is also a poor conductor of heat, so wooden doors are suitable for moderate climates.
Aluminium
Aluminium sliding doors are known for their durability, low maintenance, and contemporary look. They are lightweight, making them easy to maneuver, and corrosion-resistant, which is ideal for coastal or high-moisture areas.
Aluminium doors can be powder coated in various colors to match the architectural style, and they often feature large glass panes for a sleek, modern appearance. One drawback of aluminium is its heat conductivity, making it less energy-efficient than other materials. However, thermally broken aluminium frames with insulating materials can improve the door’s energy efficiency.
Steel
Steel sliding doors are becoming increasingly popular due to their strength, security, and stylish looks. They are highly durable, resistant to warping and rotting, and provide excellent security against potential break-ins.
Similar to aluminium, steel doors can be powder coated in different colors, and they usually feature large glass panes for an open and modern aesthetic. Steel doors are better thermal conductors than aluminium but still have some energy-efficiency concerns. Installing insulated glass can help counteract this issue. Additionally, steel doors can be prone to rust if not adequately maintained, especially in coastal or high-moisture areas.
Vinyl
Vinyl sliding doors are affordable, low-maintenance, and energy-efficient options. Made from PVC (polyvinyl chloride), these doors are resistant to moisture, warping, and rotting, which makes them suitable for various climate conditions. They are available in a wide range of colors and finishes, although the options may be more limited compared to wood or aluminium doors.
One advantage of vinyl doors is their excellent insulation properties, making them ideal for energy-efficient homes. They are also easy to clean and maintain as they don’t require painting or staining. The downside is that over time, vinyl can fade or become discolored under harsh weather conditions or direct sunlight exposure.
Fiberglass
Fiberglass sliding doors are an excellent alternative for those who desire the appearance of wood without the high maintenance requirements. They are made from composite materials that mimic the texture and grain of real wood but are resistant to weathering, warping, rotting, and termite damage.
Fiberglass doors are energy efficient, with good insulation properties and the ability to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations. They can be easily customized in terms of size, style, and finish and require minimal maintenance. The main drawback of fiberglass doors is their higher initial cost compared to other materials like vinyl or aluminium. However, this investment may be worthwhile given their durability and long-lasting performance.
Advantages of Different Sliding Door Configurations
Sliding doors have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their numerous advantages, including space-saving design, increased natural light, improved indoor-outdoor flow, energy efficiency, and enhanced aesthetic appeal. In this article, we will explore the advantages of various sliding door configurations so you can make an informed decision for your space.
Space-Saving Design
One of the most apparent advantages of sliding door configurations is the space-saving design. Traditional hinged doors can consume valuable floor space, especially in smaller rooms, with their need for a swing radius. Sliding doors, on the other hand, glide seamlessly along a track, eliminating the requirement for additional space.
Different sliding door configurations offer varying levels of space-saving functionality. For instance, pocket sliding doors retract completely into the adjacent wall, making them a perfect solution for tight spaces or partitioning open floor plan areas. Bi-fold sliding doors, commonly used for patios and balconies, can partially fold, taking up less space when opened.
No matter the sliding door configuration, they provide the benefit of opening up floor space, allowing for more flexible room layouts and furnishings.
Increased Natural Light
A significant advantage of sliding door configurations is the introduction of more natural light into a space. By incorporating larger glass panels or even floor-to-ceiling designs, sliding doors allow for a more significant amount of sunlight to enter a room, creating a bright, welcoming atmosphere.
Various configurations cater to different levels of light, depending on the desired outcome. For example, a sliding glass wall is a configuration where an entire wall can be replaced with expansive glass panels, providing an unparalleled level of natural light.
Not only does the increased natural light make a space feel more inviting, but it can also contribute to mental health and productivity benefits associated with exposure to sunlight.
Improved Indoor-Outdoor Flow
Another advantage of sliding door configurations is their ability to create a seamless flow between indoor and outdoor spaces. In homes with gardens or patios, sliding doors can be used to visually and physically connect the two, allowing for a more fluid transition between the interior and exterior.
Many contemporary home designs utilize sliding doors, such as large bi-fold doors or stacking configurations, to create an almost entirely open wall, perfect for al fresco dining and entertaining.
This connectivity not only enhances the overall aesthetic but also has practical implications, like extending living areas and improving the general flow of a home.
Energy Efficiency
With energy efficiency becoming an increasingly essential consideration for homeowners, sliding door configurations can offer a range of benefits in this area. The use of large glass panels, coupled with energy-efficient glass options like double glazing, can improve a home’s insulation and assist in maintaining consistent interior temperatures.
The increased natural light provided by sliding door configurations can also reduce the need for artificial lighting during the daytime, leading to decreased energy consumption and electricity costs.
By carefully selecting the materials, glass options, and design elements, homeowners can enhance the energy efficiency of their sliding door configuration and minimize their environmental impact.
Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal
Finally, sliding door configurations can significantly contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal of a space. With a variety of designs, materials, and finishes available, sliding doors can be tailored to complement a wide range of architectural styles and interior decor themes.
Modern sliding door configurations offer sleek lines and minimalist designs, which can elevate the appearance of contemporary homes. In contrast, more traditional styles can be achieved through the use of materials such as timber and decorative glass elements.
In conclusion, the various sliding door configurations available provide numerous advantages in terms of space-saving design, increased natural light, improved indoor-outdoor flow, energy efficiency, and enhanced aesthetic appeal. By carefully considering your unique space and requirements, you can choose a sliding door configuration that best meets your needs and adds value to your property.
Choosing the Right Sliding Door Configuration
Selecting the perfect sliding door configuration for your home or office involves considering various factors. The overall layout, architectural style, intended usage, climate considerations, and budget constraints are all essential aspects that can influence your decision. In this article, we will explore each of these aspects to help you make an informed choice for your sliding door configuration.
Available Space and Room Layout
The available space in a room and the overall layout determine the type and size of sliding doors suitable for your requirement. Begin by measuring the opening width and height where you intend to place the sliding doors. Keeping these measurements in mind helps you in identifying an appropriate configuration.
For smaller rooms, a single-panel sliding door or a two-panel configuration might be a better fit, while larger rooms can accommodate three or four-panel sliding doors. Additionally, consider the positioning of the sliding door in relation to the furniture and fixtures. Make sure to account for enough clearance space to allow a smooth opening and closing movement.
Finally, evaluate the traffic patterns in your room to determine the ideal direction of the sliding door. You may want to choose between left or right openings or a bi-parting configuration where door panels slide on both ends.
Architectural Style and Design Preferences
The aesthetic look of the sliding door plays a significant role in complementing the overall style and design of your home or office space. Evaluate the interior design and architectural style of your space to determine which sliding door configuration will blend seamlessly and enhance its appeal.
For instance, if your home reflects a modern and minimalist design style, opt for sleek, frameless glass sliding doors. On the other hand, a traditional or rustic style décor can benefit greatly from wooden or aluminium framed sliding doors.
Additionally, an extensive range of door panel materials, finishes, and colors are available to match your preferences. Transparent, frosted or etched glass sliding doors offers various design options to cater to your individual taste.
Intended Usage and Functional Requirements
Understanding the intended usage and functional requirements of the sliding door in your space helps in narrowing down the right configuration. For instance, if you plan to divide a room or create a private space, opt for a configuration with solid panels or stained glass for added privacy.
On the other hand, if you wish to create an unobstructed view of your garden or patio, a full glass sliding door with minimal framing could be your best bet. Prioritizing energy efficiency and insulation properties may lead you toward sliding doors with double or triple-glazed glass panels or insulated aluminium panels.
Climate and Weather Considerations
The climate and weather conditions of your region also play an essential role in choosing a sliding door configuration. For areas with extreme temperatures, choose sliding door materials that offer excellent insulation and energy efficiency, such as double-glazed glass or insulated aluminium.
In coastal regions or areas exposed to harsh weather elements, opt for sliding doors with weather-resistant materials such as corrosion-resistant aluminium or weatherproofing seals. These help in protecting your sliding doors from the undesirable effects of moisture, humidity, and temperature fluctuations.
Budget and Cost Factors
Budget and cost constraints are other vital aspects to consider when choosing a sliding door configuration. The material, size, and complexity of the design are some factors that can affect the overall cost of the door.
Keep in mind that while certain configurations may seem more expensive upfront, they can save money in the long run through better energy efficiency, durability, and low maintenance requirements. Opt for a sliding door configuration that strikes the perfect balance between cost-effectiveness and quality while meeting your specific requirements.
Installation and Maintenance of Sliding Door Configurations
Sliding doors have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their aesthetic appeal and space-saving functionality. They are commonly used in both residential and commercial settings, such as in homes, offices, and hotels. However, for sliding doors to function optimally, proper installation and maintenance are necessary. This article will discuss the installation process, regular cleaning and maintenance, troubleshooting tips, and how to replace parts and upgrade components.
Proper Installation Techniques
A critical aspect of installing a sliding door is ensuring its correct alignment; otherwise, it may not slide smoothly or securely. Here are a few essential installation steps to follow:
- Choose the appropriate track system according to the weight of your door and the material of your wall or ceiling. Consult with a professional to ensure the proper selection of hardware.
- Prepare the area where the sliding door will be installed. Ensure the wall, floor, and ceiling are clean and free of obstructions.
- Use a level to mark a straight line on the wall, ceiling, or floor where the sliding door track will be mounted. This process ensures accurate alignment and helps prevent problems associated with uneven mounting.
- Install the door track according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Attach all brackets and supports securely to provide adequate support for the door’s weight.
- Install door rollers and other hardware (such as stops, door guides, or soft closures) onto the door panel before hanging it onto the track. Make sure the panel is aligned correctly and slides smoothly.
- Test the sliding door to confirm that it opens and closes smoothly and securely. Adjust the rollers as needed to achieve optimal performance.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
To ensure the smooth and safe operation of a sliding door, regular maintenance and cleaning are crucial. Here are some basic maintenance tips:
- Clean the track: Remove any debris or dust buildup from the track with a soft brush or vacuum attachment. Use a damp cloth and mild detergent to clean greasy or dirty tracks to allow smooth sliding.
- Lubricate the track and rollers: Apply a light layer of silicone-based lubricant to the track and rollers to reduce friction and increase lifespan.
- Inspect the hardware: Regularly check the track, rollers, and other hardware for wear and tear, such as loose screws or broken parts. Replace any damaged or worn components when necessary.
- Adjust door rollers: If the door becomes difficult to slide or starts to drag on the floor, adjust the rollers to maintain alignment and ensure smooth sliding.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Some common sliding door problems are usually resolved quickly with simple adjustments or fixes. Here are a few troubleshooting tips:
- Misaligned door: If the door does not slide smoothly or comes off the track, check the rollers and track for proper alignment. Minor adjustments can often resolve the issue.
- Sticky door: If the door is difficult to slide or sticks to the track, clean and lubricate the track and rollers.
- Damaged hardware: Inspect the track, rollers, and other hardware components for visible damage or wear. Replace any damaged parts as needed.
- Squeaking or loud noises: Lubricate the rollers and track to alleviate squeaking or excess noise.
Replacing Parts and Upgrading Components
There comes a time when you will have to replace parts or upgrade components of your sliding door system to maintain its smooth and secure operation. Here are some tips for replacing and upgrading components:
- Replacing damaged or worn hardware: Consult the manufacturer’s documentation or contact their support service to purchase the correct replacement parts for your specific sliding door system.
- Upgrading components: If you wish to enhance the aesthetics or functionality of your sliding door, consult with a professional or the manufacturer about potential upgrades available for your sliding door system.
- Professional help: If you are unsure about replacing or upgrading components yourself, it is recommended to seek professional assistance to ensure the proper installation of new parts.
Regular care and maintenance will keep your sliding door operating smoothly and efficiently, enhancing the overall appeal and functionality of your living or working space. By following these guidelines, you can ensure the longevity and reliability of your sliding door system.
FAQs on Sliding Door Configurations
What are the various sliding door configurations available?
There are several sliding door configurations, including single sliding, bi-parting, telescopic (two or four-panel), corner sliding, curved sliding, and folding (bi-fold and multi-fold) doors. These configurations provide different levels of flexibility, aesthetics, and space optimization, catering to various architectural and design preferences.
How do I choose the best sliding door configuration for my space?
Consider factors such as room layout, available space, desired opening size, ease of access, and aesthetics while selecting a sliding door configuration. Consulting with a door specialist or architect can provide an expert opinion on the best configuration for your specific space and requirements.
What is a telescopic sliding door configuration and how does it differ from other configurations?
A telescopic sliding door configuration features multiple sliding door panels, with one panel sliding behind the next, either in a two or four-panel setup. It differs from other configurations, such as single sliding or bi-parting doors, by offering a wider clear opening, making it ideal for limited wall space and an unobstructed view.
Do curved sliding door configurations require a specific track system or unique hardware?
Curved sliding door configurations need a customized track system that follows the curve of the door. This curved track system is unique and differs from traditional linear tracks. Additionally, suitable roller hardware is required to ensure smooth operation of the curved sliding doors, which may be specific to the manufacturer or model.
Are bi-fold and multi-fold door configurations the same as sliding door configurations?
While both bi-fold and multi-fold door configurations are space-saving solutions, they are not the same as sliding door configurations. In bi-fold and multi-fold setups, doors are hinged together and folded, resembling an accordion when opened. In contrast, sliding door configurations have door panels that slide along tracks parallel to adjacent walls.
Can I change the configuration of my existing sliding doors without major construction work?
Minor modifications, such as converting a single sliding door to a bi-parting configuration, may be possible with limited construction work. However, significant changes, such as installing telescopic or curved configurations, typically require additional structural alterations and potentially an extensive construction process. Consulting a door specialist is advised to assess the scope of work and feasibility.
